WordPress is shipped with rest API which makes migrating or importing contents into WordPress sites very easy. If you have bulk contents for example 100s of posts. It’s not possible to create post manually however you can use rest API features to automate the task.
There are few things required before importing contents,
- Basic – Auth Plugin: https://github.com/WP-API/Basic-Auth
- Python >= 3
- Administrator username and password of your WordPress site.
Basic-Auth plugin is very useful while using WordPress’ rest API. Unfortunately, it is not hosted on the WordPress site. So you can not search and install from the WordPress admin dashboard. Therefore you have to manually download and install it. Here’s the instruction on how to install https://github.com/WP-API/Basic-Auth

After you have successfully installed you are ready to use the admin username and password for rest API.
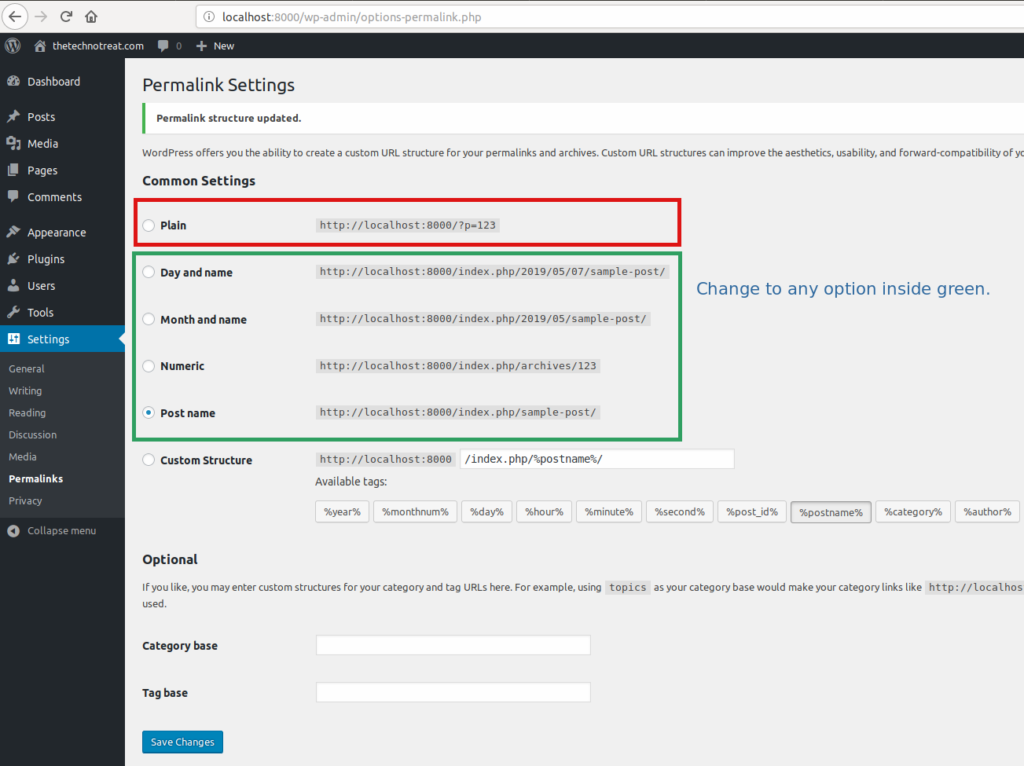
You also need to change permalink settings. Under common settings choose any type other than ‘Plain’. WordPress has ‘Plain’ selected by default. Change it to anything except ‘Plain’.
I am using python3.6 to handle the API request. You can use any other programming language or even simple Curl request can do the job if you know how to use it.
I have created a python class and setup localhost at http://localhost:8000
Python library used here are requests, CSV and JSON. You only need to install requests (https://pypi.org/project/requests/). Others are available by default in python3 and above.
import requests
import csv
import jsonAfter importing python libraries here’s the code for initializing class.
class WordPress(object):
"""Docstring for MyClass. """
def __init__(self, domain, username, password):
"""
:username: wordpress username
:password: wordpress password
:domain: wordpress domain name | eg: http://thetechnotreat.com
"""
self.domain = domain
self._username = username
self._password = password
self.request = requests.session()
self.request.auth = (self._username, self._password)Note that user must have administrator privilege or it won’t be able to create posts.
Function to create post
def upload_post(self, title, body, category):
"""create new post
:title: post title
:body: post body
:category: category ids
:returns: created post detail (dict)
"""
info = dict()
info['title'] = title
info['content'] = body
info['categories'] = ",".join(category)
response = self.request.post(self.domain+'/wp-json/wp/v2/posts', json=info)
return_text = json.loads(response.text)
return return_textupload_post function takes three arguments. ‘title’ is the title of the post, ‘body’ is the main content of the post and ‘category’ is the category of the post. While creating a post with its category, rest API takes category id rather than category name. So there must be a category already created on site before creating a post.
Here is the function to check and create category on site.
def create_category(self, category):
"""create new category if not available
:returns: category id
"""
url = self.domain+"/wp-json/wp/v2/categories"
response = self.request.get(url)
categories = json.loads(response.text)
for cat in categories:
if cat['name'] == category:
return cat['id']
data = dict()
data['name'] = category
response = self.request.post(url, json=data)
upload_info = json.loads(response.text)
if 'id' in upload_info:
return upload_info['id']
else:
return NoneNow you just need to loop through CVS files where your collected posts are.
with open('sample_posts.csv') as csv_file:
reader = csv.DictReader(csv_file)
wp = WordPress('http://localhost:8000', 'technotreat', 'lVBO4lTmsCMd3ImQ^q')
count = 1
for post in reader:
categories = post['category'].split(",")
cat_ids = []
for c in categories:
id = wp.create_category(c)
if id:
cat_ids.append(str(id))
upload_text = wp.upload_post(post['title'], post['content'], cat_ids)
print (str(count) + " post imported")
count += 1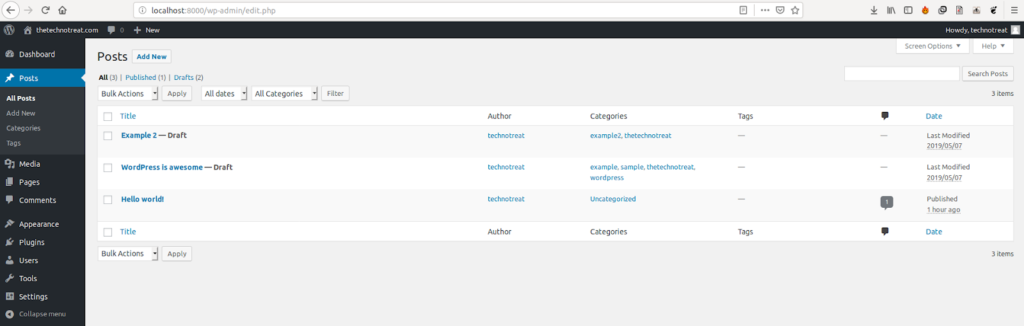
[download id=”28″]


[…] the previous tutorial, we learned about how to import content into a WordPress site. In this tutorial, I will explain […]
Some genuinely interesting info , well written and loosely user pleasant.